Decision Tree Regression¶
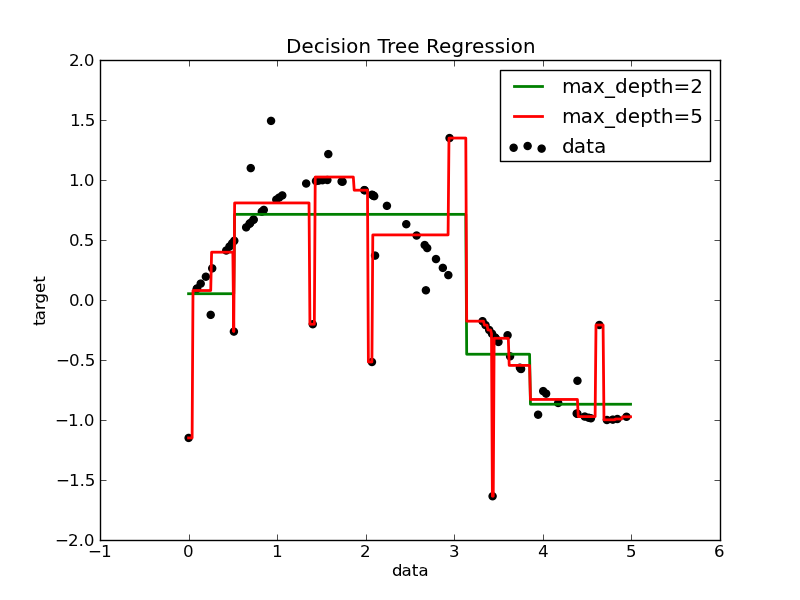
1D regression with decision trees: the decision tree is used to fit a sine curve with addition noisy observation. As a result, it learns local linear regressions approximating the sine curve.
We can see that if the maximum depth of the tree (controled by the max_depth parameter) is set too high, the decision trees learn too fine details of the training data and learn from the noise, i.e. they overfit.
Python source code: plot_tree_regression.py
print __doc__
import numpy as np
# Create a random dataset
rng = np.random.RandomState(1)
X = np.sort(5 * rng.rand(80, 1), axis=0)
y = np.sin(X).ravel()
y[::5] += 3 * (0.5 - rng.rand(16))
# Fit regression model
from sklearn.tree import DecisionTreeRegressor
clf_1 = DecisionTreeRegressor(max_depth=2)
clf_2 = DecisionTreeRegressor(max_depth=5)
clf_1.fit(X, y)
clf_2.fit(X, y)
# Predict
X_test = np.arange(0.0, 5.0, 0.01)[:, np.newaxis]
y_1 = clf_1.predict(X_test)
y_2 = clf_2.predict(X_test)
# Plot the results
import pylab as pl
pl.figure()
pl.scatter(X, y, c="k", label="data")
pl.plot(X_test, y_1, c="g", label="max_depth=2", linewidth=2)
pl.plot(X_test, y_2, c="r", label="max_depth=5", linewidth=2)
pl.xlabel("data")
pl.ylabel("target")
pl.title("Decision Tree Regression")
pl.legend()
pl.show()
