Plot Ridge coefficients as a function of the regularization¶
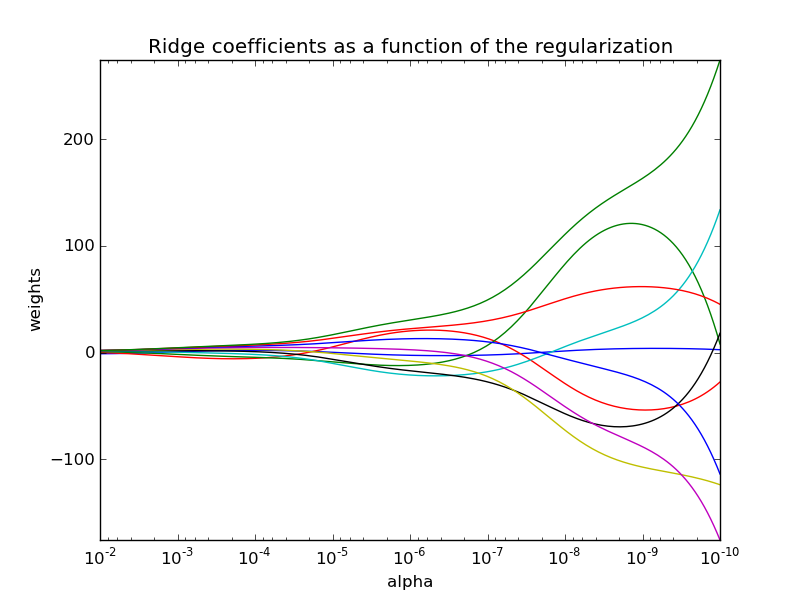
Shows the effect of collinearity in the coefficients or the Ridge. At the end of the path, as alpha tends toward zero and the solution tends towards the ordinary least squares, coefficients exhibit big oscillations.
Python source code: plot_ridge_path.py
# Author: Fabian Pedregosa -- <fabian.pedregosa@inria.fr>
# License: BSD Style.
print __doc__
import numpy as np
import pylab as pl
from sklearn import linear_model
# X is the 10x10 Hilbert matrix
X = 1. / (np.arange(1, 11) + np.arange(0, 10)[:, np.newaxis])
y = np.ones(10)
###############################################################################
# Compute paths
n_alphas = 200
alphas = np.logspace(-10, -2, n_alphas)
clf = linear_model.Ridge(fit_intercept=False)
coefs = []
for a in alphas:
clf.set_params(alpha=a)
clf.fit(X, y)
coefs.append(clf.coef_)
###############################################################################
# Display results
ax = pl.gca()
ax.set_color_cycle(['b', 'r', 'g', 'c', 'k', 'y', 'm'])
ax.plot(alphas, coefs)
ax.set_xscale('log')
ax.set_xlim(ax.get_xlim()[::-1]) # reverse axis
pl.xlabel('alpha')
pl.ylabel('weights')
pl.title('Ridge coefficients as a function of the regularization')
pl.axis('tight')
pl.show()
