SVM-Kernels¶
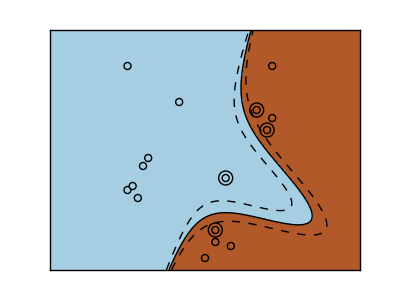
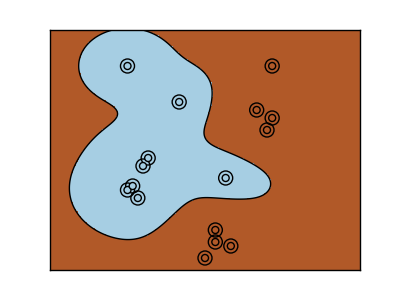
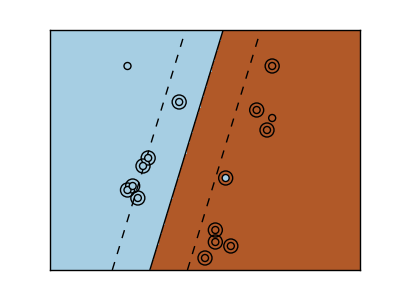
Three different types of SVM-Kernels are displayed below. The polynomial and RBF are especially useful when the data-points are not linearly seperable.
Python source code: plot_svm_kernels.py
print __doc__
# Code source: Gael Varoqueux
# License: BSD
import numpy as np
import pylab as pl
from sklearn import svm
# Our dataset and targets
X = np.c_[(.4, -.7),
(-1.5, -1),
(-1.4, -.9),
(-1.3, -1.2),
(-1.1, -.2),
(-1.2, -.4),
( -.5, 1.2),
( -1.5, 2.1),
( 1, 1),
# --
( 1.3, .8),
( 1.2, .5),
( .2, -2),
( .5, -2.4),
( .2, -2.3),
( 0, -2.7),
( 1.3, 2.1),
].T
Y = [0]*8 + [1]*8
# figure number
fignum = 1
# fit the model
for kernel in ('linear', 'poly', 'rbf'):
clf = svm.SVC(kernel=kernel, gamma=2)
clf.fit(X, Y)
# plot the line, the points, and the nearest vectors to the plane
pl.figure(fignum, figsize=(4, 3))
pl.clf()
pl.set_cmap(pl.cm.Paired)
pl.scatter(clf.support_vectors_[:, 0], clf.support_vectors_[:, 1],
s=80, facecolors='none', zorder=10)
pl.scatter(X[:,0], X[:,1], c=Y, zorder=10)
pl.axis('tight')
x_min = -3
x_max = 3
y_min = -3
y_max = 3
XX, YY = np.mgrid[x_min:x_max:200j, y_min:y_max:200j]
Z = clf.decision_function(np.c_[XX.ravel(), YY.ravel()])
# Put the result into a color plot
Z = Z.reshape(XX.shape)
pl.figure(fignum, figsize=(4, 3))
pl.set_cmap(pl.cm.Paired)
pl.pcolormesh(XX, YY, Z > 0)
pl.contour(XX, YY, Z, colors=['k', 'k', 'k'],
linestyles=['--', '-', '--'],
levels=[-.5, 0, .5])
pl.xlim(x_min, x_max)
pl.ylim(y_min, y_max)
pl.xticks(())
pl.yticks(())
fignum = fignum + 1
pl.show()